Table of contents:
If not the “heart”, a microcontroller is undoubtedly the “brain” of any IoT device. The choice of microcontrollers in a market is huge, while there are obvious leaders. These are ESP8266, ESP32, Raspberry Pi, and Arduino. We tell you how to choose a microcontroller for your task and what advantages and disadvantages different MCUs have.
Which microcontroller to choose: pros and cons of ESP8266, ESP32, Raspberry Pi, and Arduino
ESP8266 & ESP32
These microcontrollers are manufactured by the Chinese company Espressif Systems, and ESP32 is the apparent leader in the pair. ESP8266 is an outdated model that loses to its counterpart in almost all parameters. It is worth mentioning because many DIY enthusiasts continue to create ESP8266-based projects. Sometimes because they are satisfied with the characteristics of this MCU, sometimes because of cheapness, sometimes purely by inertia. Many projects were once created based on such a microcontroller, and they continue to live and develop.
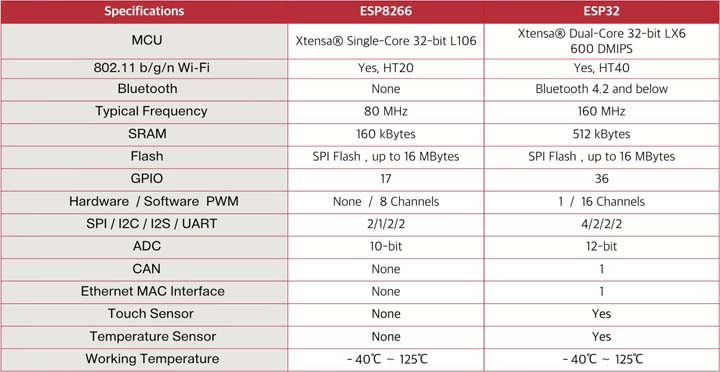
The key characteristics of both models can be found in the table below. It can be seen that ESP8266 loses in everything. Therefore, there is no point in continuing to talk about it. Let’s stop at ESP32, which is better for creating new projects.
After the advent of ESP, these microcontrollers were considered difficult to develop for a long time – knowledge and programming skills were required to write the device’s firmware. Now, this is a little less relevant. Firstly, a simple ESPHome tool has appeared, and secondly, ESP can be made to work using the Arduino IDE development environment.
Advantages of ESP32:
- they are supplied as separate chips and as development boards; the latter is convenient when working on a prototype;
- multiplexing, when multiple functions can be set for each of the 36 I/O pins;
- and yes, 36 pins is a separate advantage; ESP8266 had only 17 of them, which is catastrophically small;
- built-in Wi-Fi module;
- support for Bluetooth 4.2 and Bluetooth low energy;
- touch contacts that can be used to wake up the microcontroller from a deep sleep;
- built-in Hall effect sensor;
- you can find microcontrollers with a temperature sensor, although the manufacturer at some point removed it from the circuit;
- support for analog sensors;
- a lot of tools for creating firmware: the Arduino IDE environment, a special Python implementation – MicroPython, an ESPHome environment that does not require programming, and others;
- designed for energy saving;
- low cost.
Disadvantages of ESP32:
- support only Wi-FI networks with a frequency range of 2.4 GHz – they will not connect to a modern 5 GHz network.
Raspberry Pi
This is not exactly a microcontroller, or rather, not only it. Raspberry Pi is a full-fledged single-board computer that appeared in 2012 as an educational project. However, the development of the British from the Raspberry Pi Foundation turned out to be so successful that even the developers of commercial products appreciated it.
In fact, the Raspberry Pi is a small computer with a Linux operating system. This is a huge advantage since you can run a ready-made complex application on a Raspberry Pi.
The big plus of the project is that it does not stand still. New versions of Raspberry Pi are released annually, and processor frequency, memory capacity, and other characteristics are growing.
Advantages:
- built-in Wi-Fi module in most modern models;
- built-in Bluetooth low energy module in most models;
- you can use Linux applications if the project requires it: such as nginx or Apache web servers, VPN services, photo editors, office packages;
- the possibility of expanding the circuit due to hardware accessories and additional boards;
- detailed documentation, lessons, and ready-made libraries, as well as a huge community of developers; only a lazy person will not understand Raspberry Pi;
- standard HDMI ports, 3.5mm audio, 4 USB.
Disadvantages:
- there is no built-in analog-to-digital converter, so it is tough to connect analog sensors;
- relatively high cost.
Let’s collaborate
We’re empower your business with our technology expertise
Arduino
Arduino as a class is the oldest platform of all that we are considering. It appeared back in 2005 through the efforts of the Italian company of the same name. Arduino comes in pre-built boards, much like ESP32-based development boards. This MCU cannot be used as a separate microcontroller chip for installation in an IoT device.
The principal value of Arduino today is the Arduino IDE integrated development environment. It allows you to create Windows, macOS, or Linux programs and upload them to the microcontroller. And not only on Arduino boards, since you can create a program for ESP32 using the Arduino IDE.
Advantages:
- lots of detailed documentation, ready-made libraries, and lessons on Arduino IDE,
- the actual Arduino IDE environment is easy to learn,
- installation of expansion cards, sensors, and other additional peripherals is provided,
- Many board models are equipped with built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth modules.
Disadvantages:
- weak processor characteristics and modest built-in memory, which is why Arduino is not suitable for all tasks,
- some models do not have a built-in Wi-Fi module, which is critical for IoT projects.
Which MCU is better?
When creating new products in 2Smart Cloud, you can use any microcontrollers, including those not mentioned in this article. It is enough to provide an Internet connection (using a Wi-Fi module, cable, or other methods) and write a compatible firmware. It doesn’t matter what programming language you use. You only need a library to work with MQTT, available in all modern languages.
2Smart Cloud recommendation is ESP32
Our recommendation is the ESP32 microcontroller. This is a key MCU that we use for our projects (such as an IoT access management system). ESP32 is an inexpensive device that can be used both as a development board at the prototype stage and as a chip for installation in a finished product.
When working on an ESP32 prototype, using the Arduino IDE development environment often makes sense. Programs created using it are compatible with this microcontroller, and it is relatively easy to write firmware on the Arduino IDE. It is easy to find examples of ready-made solutions and detailed documentation on this development environment on the network.
An alternative option available only for ESP is the ESPHome environment mentioned above, which allows you to create firmware even without knowledge of the basics of programming. There is also detailed documentation for this tool and many examples of ready-made solutions. Often a simple device can be started by simply copying the necessary lines of code from the examples found on the network.
Please note that in 2Smart Cloud, you can use ESPHome as a tool for creating a professional product. There will be no Wi-Fi credentials in the production firmware; they are specified when the device is paired with a mobile application.
It makes sense to use other firmware development tools for later iterations of the prototype and the final version of the device. For example, in 2Smart Cloud, developers have access to the C++ SDK and detailed documentation on working with it.
ESP8266 – acceptable, but not all tools are available
If we talk about ESP8266 microcontrollers, this is also a valid option. You will be able to create an IoT device in 2Smart Cloud, although there is no SDK and ESPHome support for microcontrollers of this series on our custom IoT development software.
We wrote firmware for ESP8266-based Sonoff devices, and they work stably as 2Smart Cloud devices.
Raspberry Pi – if you need more power
If the ESP32 characteristics are insufficient for your project, we recommend Raspberry Pi. For compatibility with 2Smart Cloud, use the NodeJS-based SDK.
Don't forget to share this post!
Read Next
Let’s dive into your case
Share with us your business idea and expectations about the software or additional services.