Table of contents:
The Internet of Things architecture implies at least three levels: IoT devices (”things”), an edge gateway, and the cloud. IoT platforms provide the two highest levels that devices communicate with using specific protocols. Let’s figure out how to connect IoT devices to the cloud. What criteria should be used to choose a connection standard, and what are the pros and cons of popular protocols?
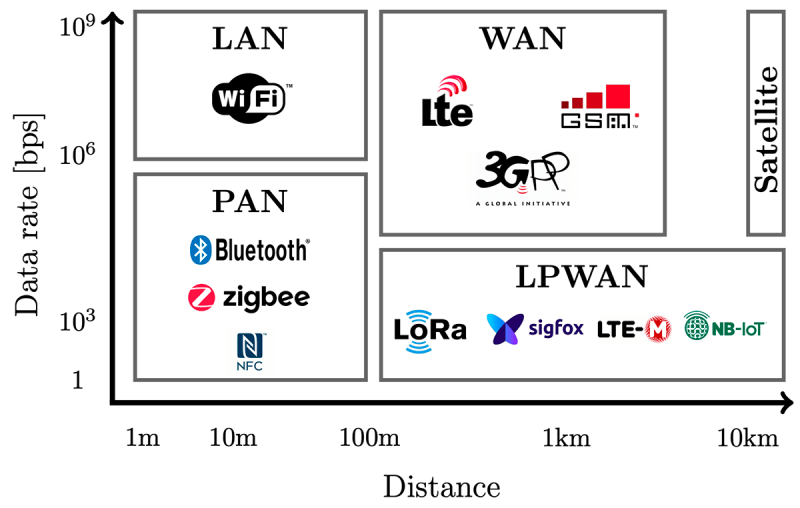
Criteria for choosing the method of connecting IoT devices
When selecting the best way to connect and control an IoT device, manufacturers focus on three critical criteria:
- power usage,
- range,
- bandwidth.
Which of the existing connection protocols is optimal depends on the device’s specifics. For example, the well-known Wi-Fi data exchange protocol is suitable for IoT devices located in the home or office and permanently connected to the power grid. Its main advantage is the low cost of operation. Disadvantages are constant energy consumption and limited range. These are serious disadvantages that limit Wi-Fi use in the world of the Internet of Things.
An energy-efficient protocol is required if the device cannot be permanently connected to the power grid. So, the BLE standard is better for small sensors – they can work from a miniature tablet-type battery for more than a year.
These are examples that relate to small-range networks. If a long-range is needed to deploy IoT solutions, different protocols are used. Let’s consider them in more detail.
Protocols for connecting and management of IoT devices
For short-range networks
Short-range networks are used in small environments – primarily at home, offices, and small compactly located enterprises. These are economical networks, most of which are characterized by low power consumption.
Bluetooth
This protocol can transmit voice and data at high speed within a 10-meter range. It is most often used to unite various devices around one user: smartwatches, wireless headsets, and fitness bracelets.
BLE
A kind of Bluetooth with significantly reduced power consumption and an extended range of up to 100 meters. It is used in consumer electronics to transmit sensor data – for example, in wireless temperature sensors.
Bluetooth 5
A standard initially focused on IoT devices. It has a higher data transfer rate than Bluetooth 4 and a more extended range of 200 meters.
NFC
A set of protocols provides data transmission at low speed and a short distance (up to 40 mm). It is used as an auxiliary when two devices interact.
Wi-Fi/802.11
A standard option for small environments. It is inexpensive to operate but requires constant energy consumption. The protocol is used in IoT devices connected to the power grid, such as “smart” lamps, sockets, and household IoT devices.
Z-Wave
A low-power wireless protocol for connecting devices to each other. It is used for environmental monitoring and control IoT devices for smart homes or commercial facilities.
Zigbee
A low-power protocol is used for simple device communication and for creating low-cost personal area networks with small digital radios. It is suitable for control and surveillance and for applications requiring secure data transmission.
Let’s collaborate
We’re empower your business with our technology expertise
For long-range networks
In smart city systems, medicine, and extensive industrial facilities, LPWAN (Low-power Wide-area Network) networks are used. They are energy-efficient long-range networks. LPWAN networks are built on a principle reminiscent of the architecture of mobile communication networks when individual devices are connected to the base station (the “star” topology). Large networks are built on the “star of stars” principle when base stations are combined into a higher-level network.
The main advantage of LPWAN is its long range, which reaches 10-15 km. The main disadvantage is the relatively low bandwidth due to a low-frequency radio channel. This disadvantage is becoming less relevant with the advent of new LPWAN protocols.
Internet of Things 4G LTE
An example of a wireless communication standard based on which LPWAN networks are built. 4G networks provide high power and low latency, which allows them to be used for Internet of Things scenarios in which real-time data and updates are required.
Internet of Things 5G
This is a new standard that is at the implementation stage. It can provide even higher data transfer speeds compared to 4G and connecting more devices.
Cat-0
Cost-effective networks based on 4G technology. They are the basis for Cat-M technology, which will replace the 2G standard.
Cat-1
A mobile Internet of Things standard designed to replace 3G networks. It is optimal for applications with a voice or browser interface.
LoRaWAN
A protocol for communication of mobile protected bidirectional devices powered by rechargeable batteries.
Support of the necessary protocols is an essential criterion for choosing an IoT platform
When choosing an IoT device management system, the manufacturer needs to be sure that they will be able to use the standards and protocols they need. Some solutions also require support for specific protocols, such as Wiegand, which is used in the cloud IoT access management system developed by our team.
In the case of 2Smart Cloud, you can be calm. Whatever technology you choose to connect an IoT device to the cloud, the platform will provide tools for connecting and controlling devices and the IoT monitoring system. Your product will get such features as devices notifications using the WhatsApp bot and others. The experience of our team includes, among other things, custom integration with cloud IoT platforms. An example of custom integration is the ability to connect 2Smart Standalone devices to the 2Smart Cloud.
If you don’t know which protocols are best for your solution, the platform team will provide you with expert support. You can get to know us better here.
Don't forget to share this post!
Read Next
Let’s dive into your case
Share with us your business idea and expectations about the software or additional services.