Flashing ESPHome Firmware on ESP32 Microcontroller macOS workflow
You can install the firmware on the microcontroller using Python.
Install the latest version of Python — you can download the stable release from the developer's website.
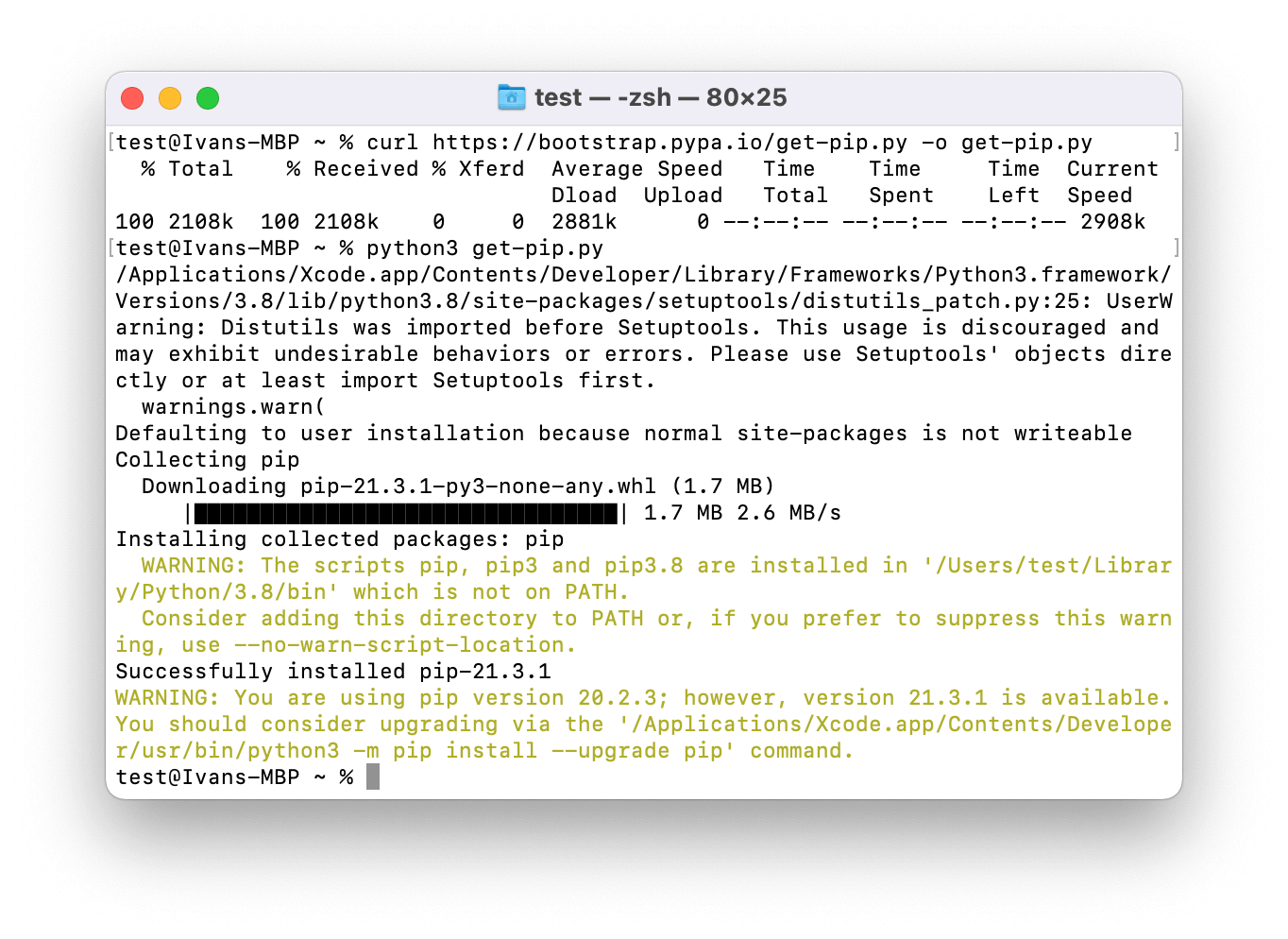
To flash the microcontroller, the pip3 package manager should be installed. Use the following command to download the pip3 installation file:
curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py -o get-pip.py
After this, install the package manager:
python3 get-pip.py
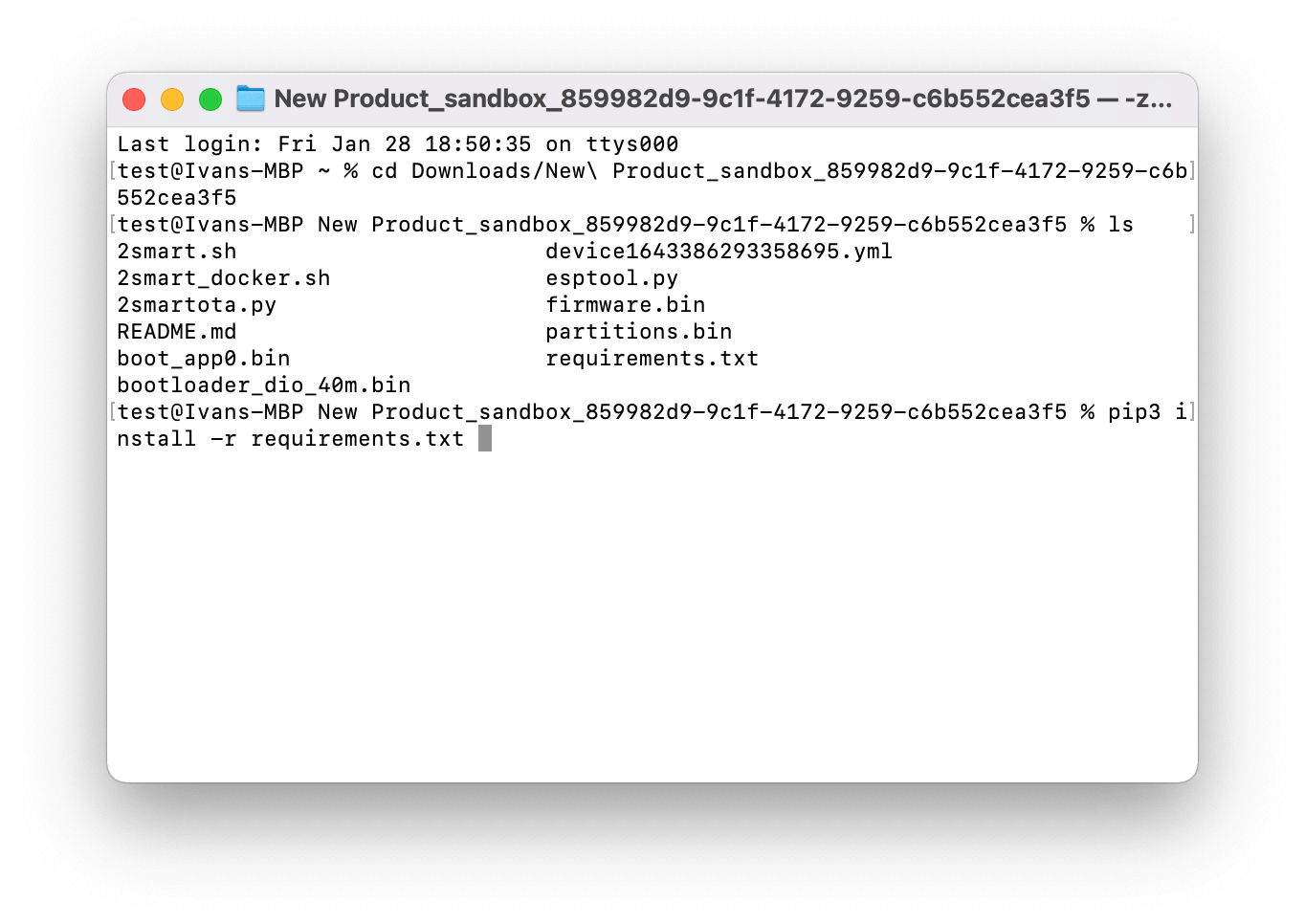
Unzip the firmware file and navigate to the directory containing the archive's firmware in the terminal.
cd Downloads/<unzipped_archive>
ls
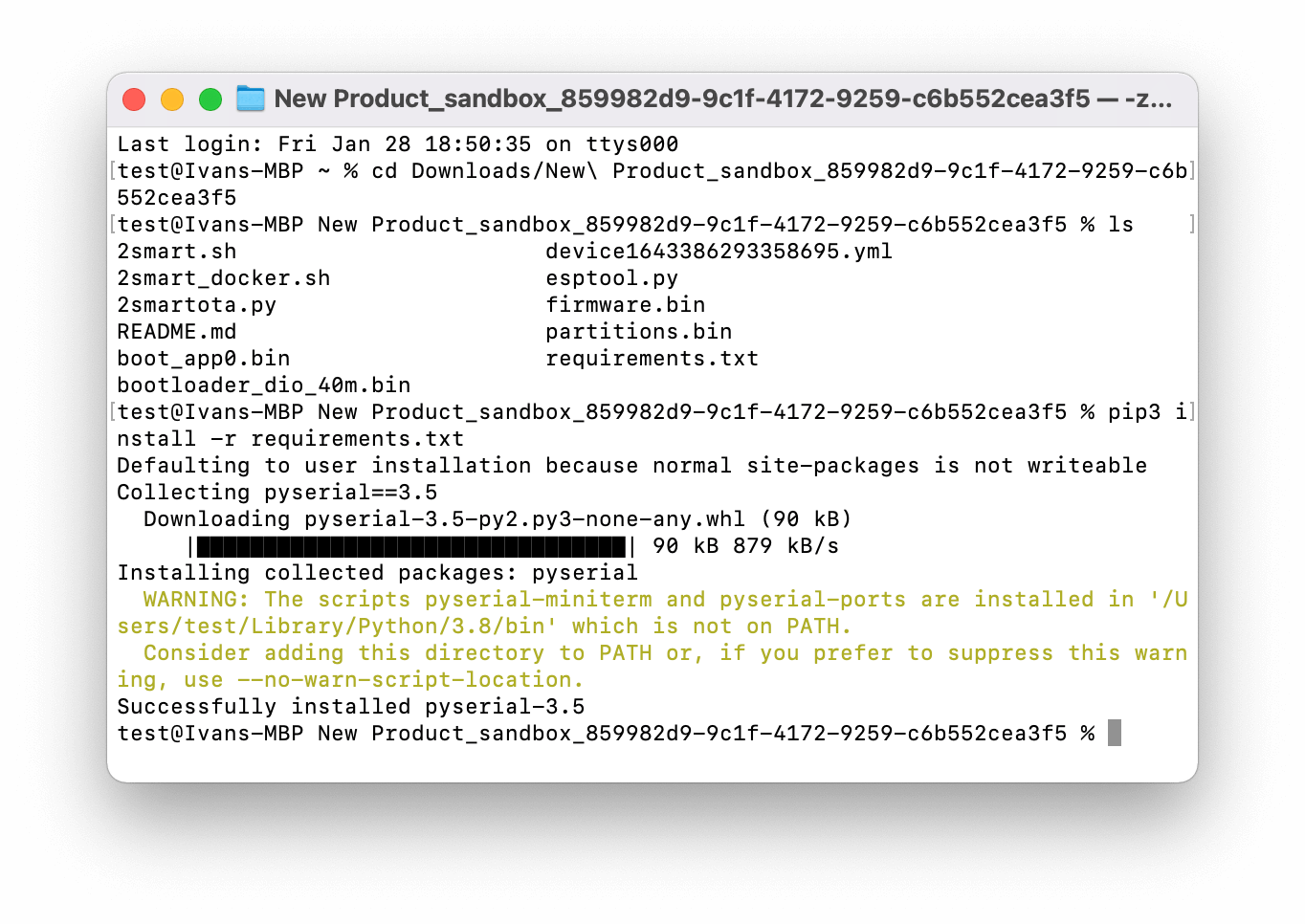
Install the necessary libraries to work with the “2smart.sh” script using the following command:
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
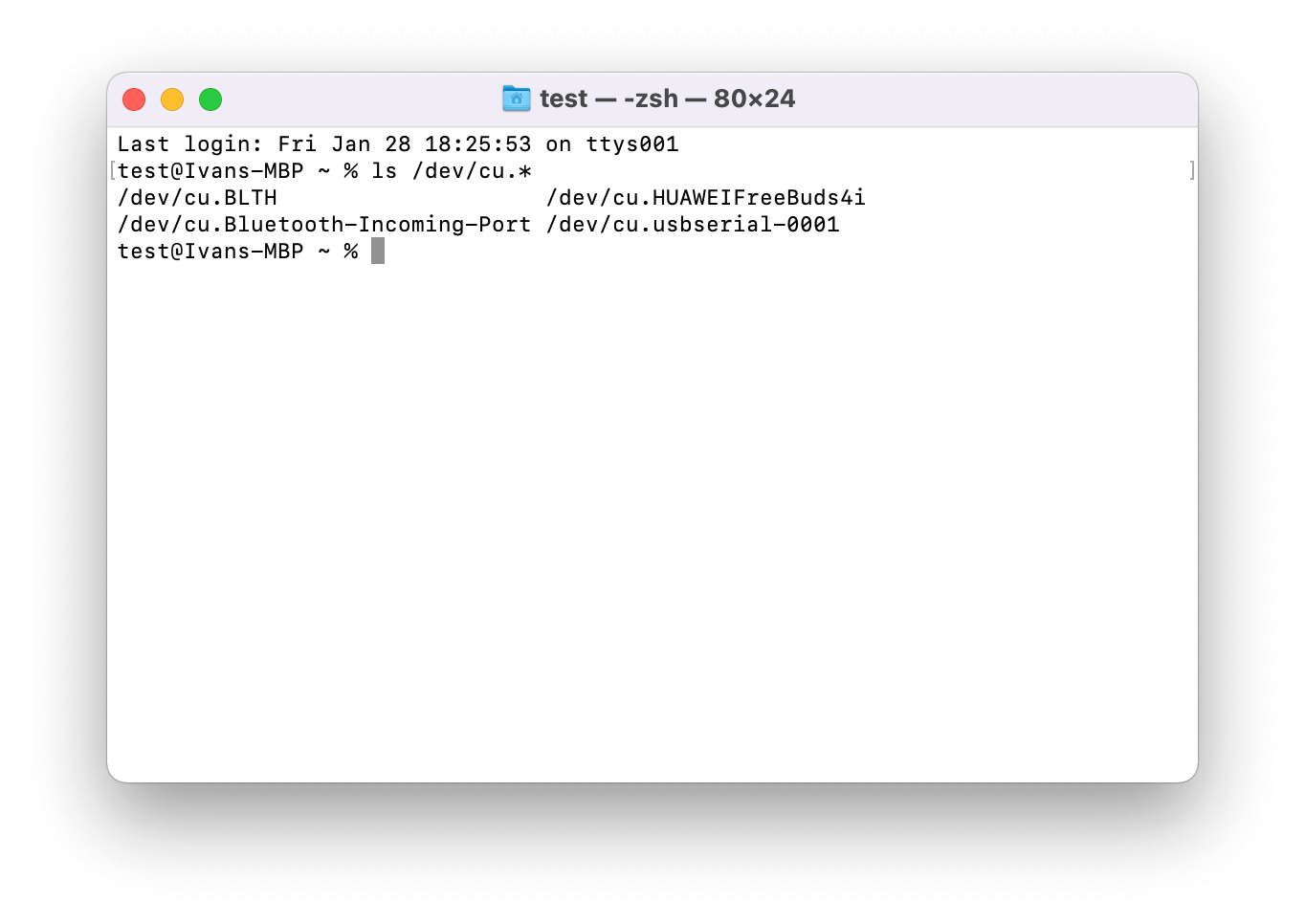
Connect your MicroUSB cable to your ESP32 Board. Then connect the other end of the USB data cable to your Mac. Enter command in the terminal:
ls /dev/cu.*
In example you should now see /dev/cu.usbserial-0001, you may choose your serial port. It is necessary for the flashing device in the next steps.
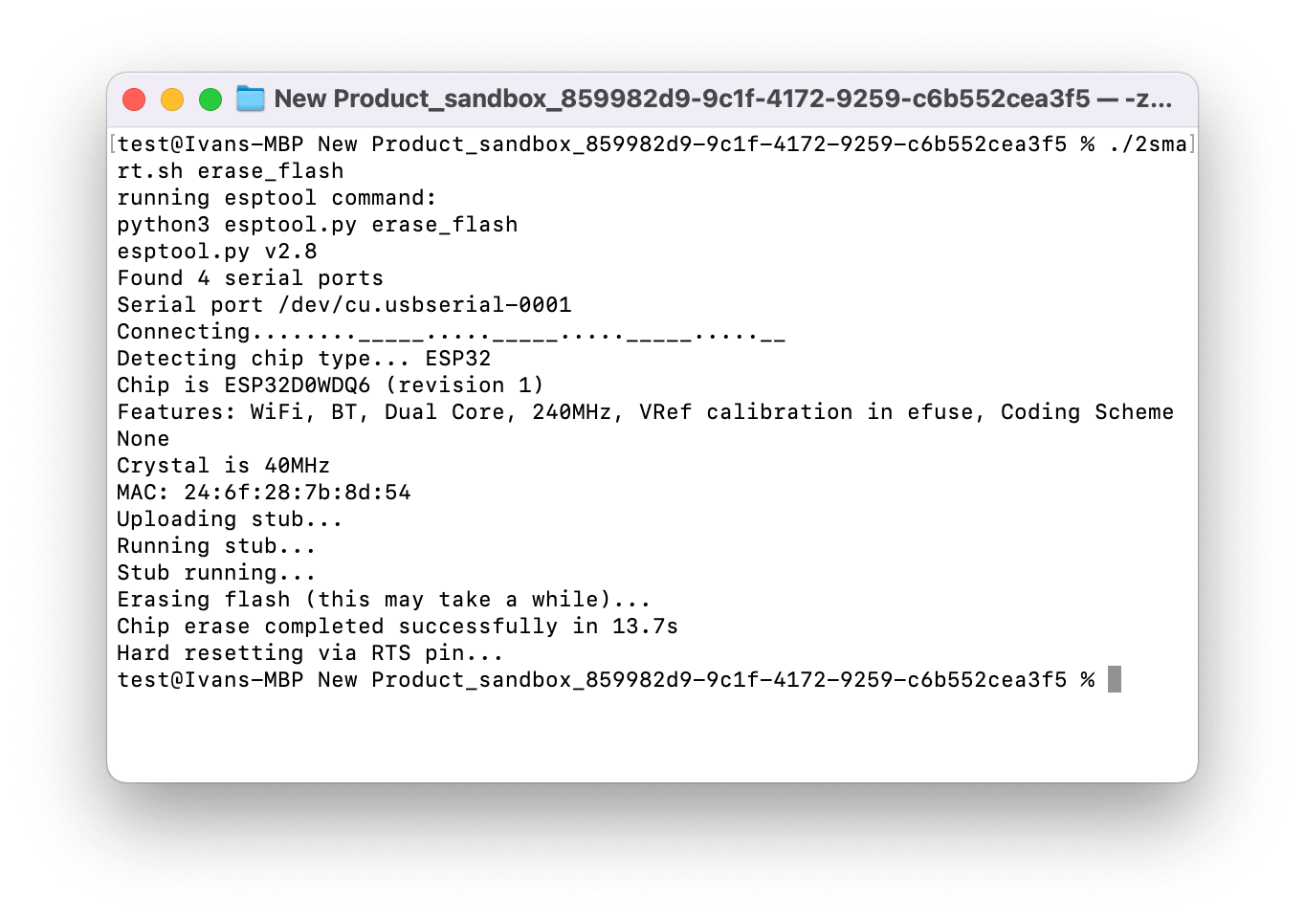
Clean up the microcontroller memory by running the following command:
./2smart.sh erase_flash
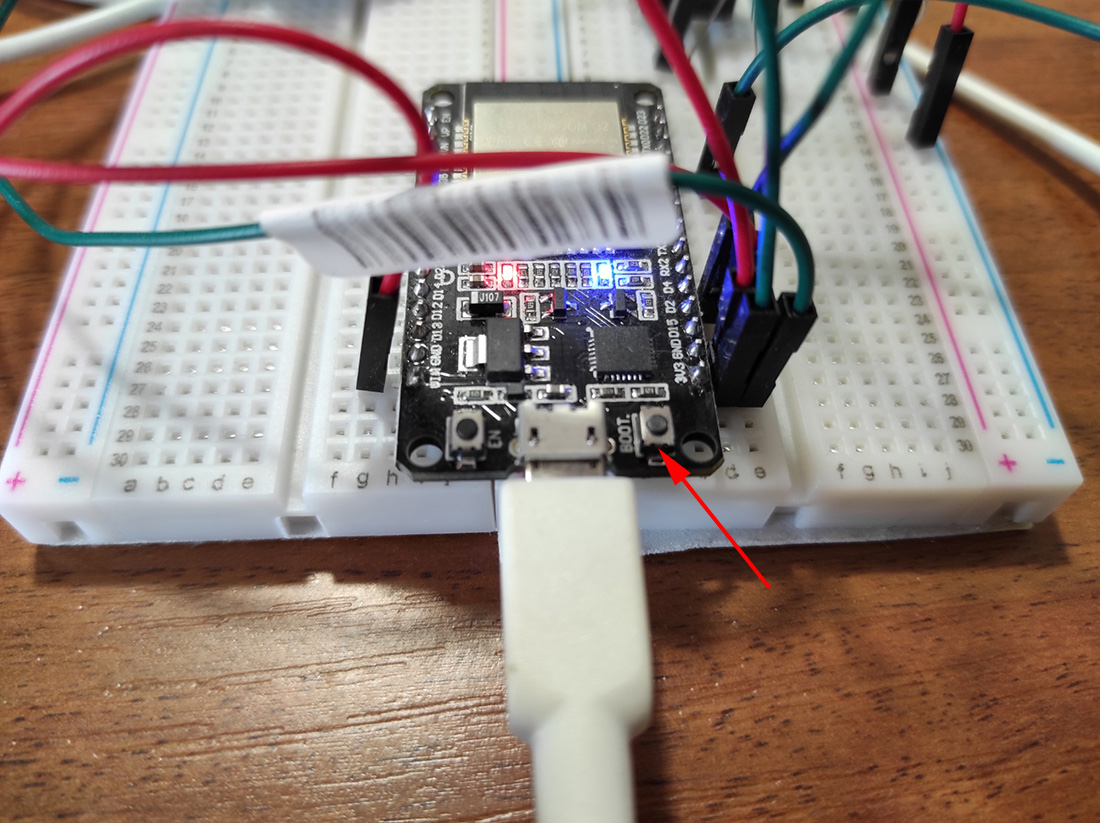
If the memory erasing stops at the “Connecting ….….” step, press the Boot button on the DevKit board:
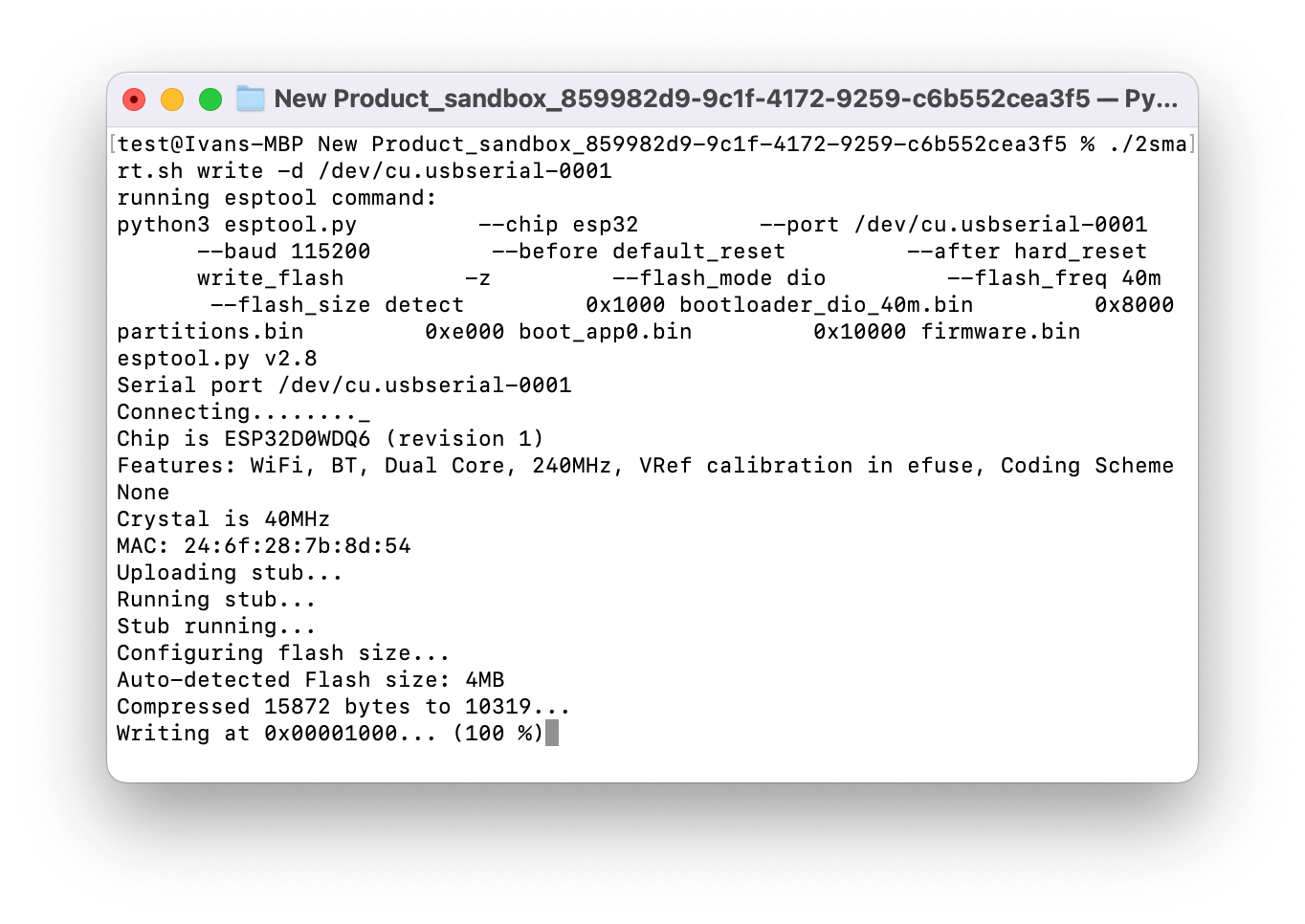
Run the “2smart.sh” script to flash the microcontroller, put your usb serial port after -d, for example /dev/cu.usbserial-0001:
./2smart.sh write -d /dev/cu.usbserial-0001
If the flashing stops at the “Connecting ….….” step, press the Boot button on the DevKit board.
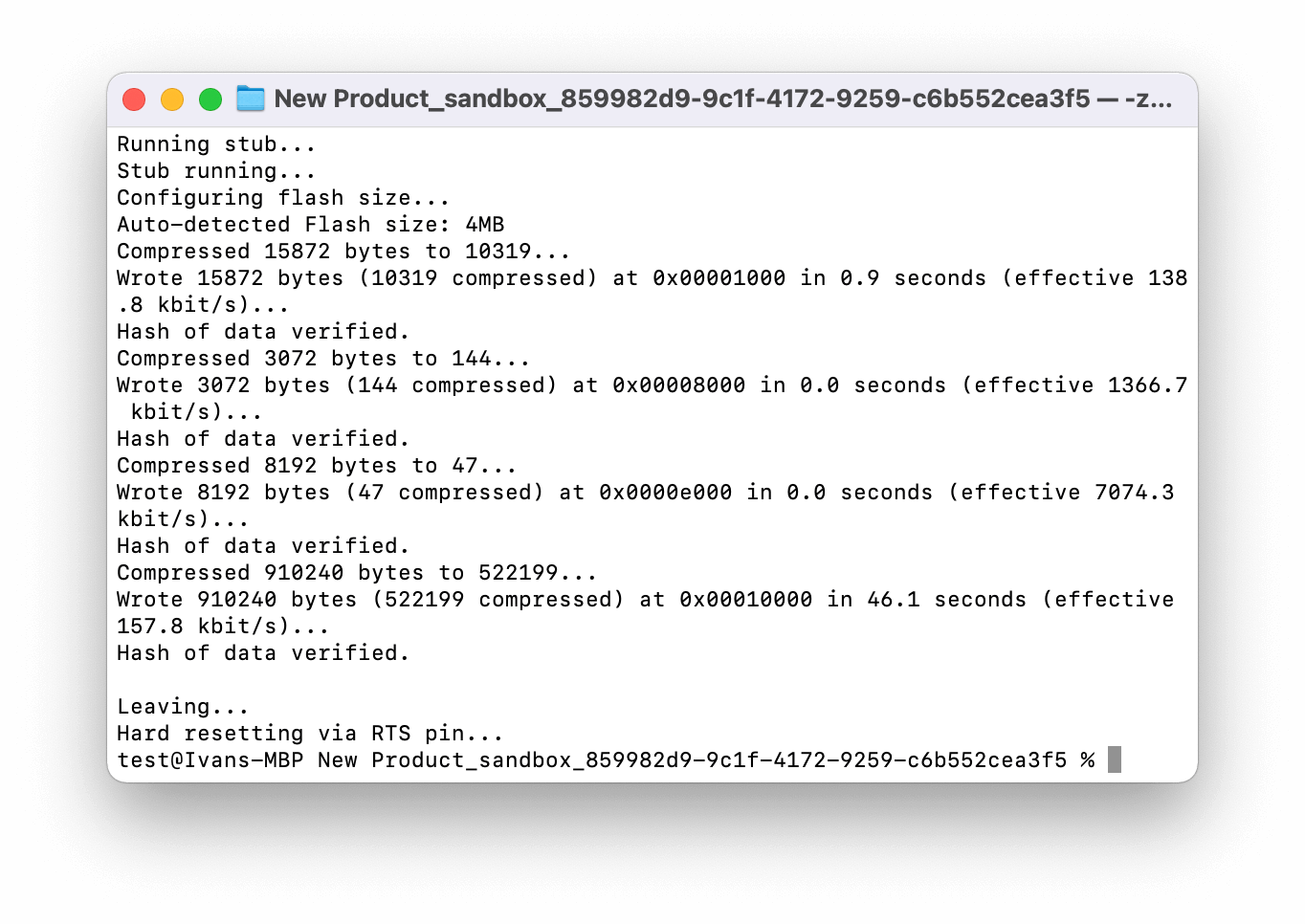
After a successful flash, you will see the “Leaving… Hard resetting via RTS pin…” notification.
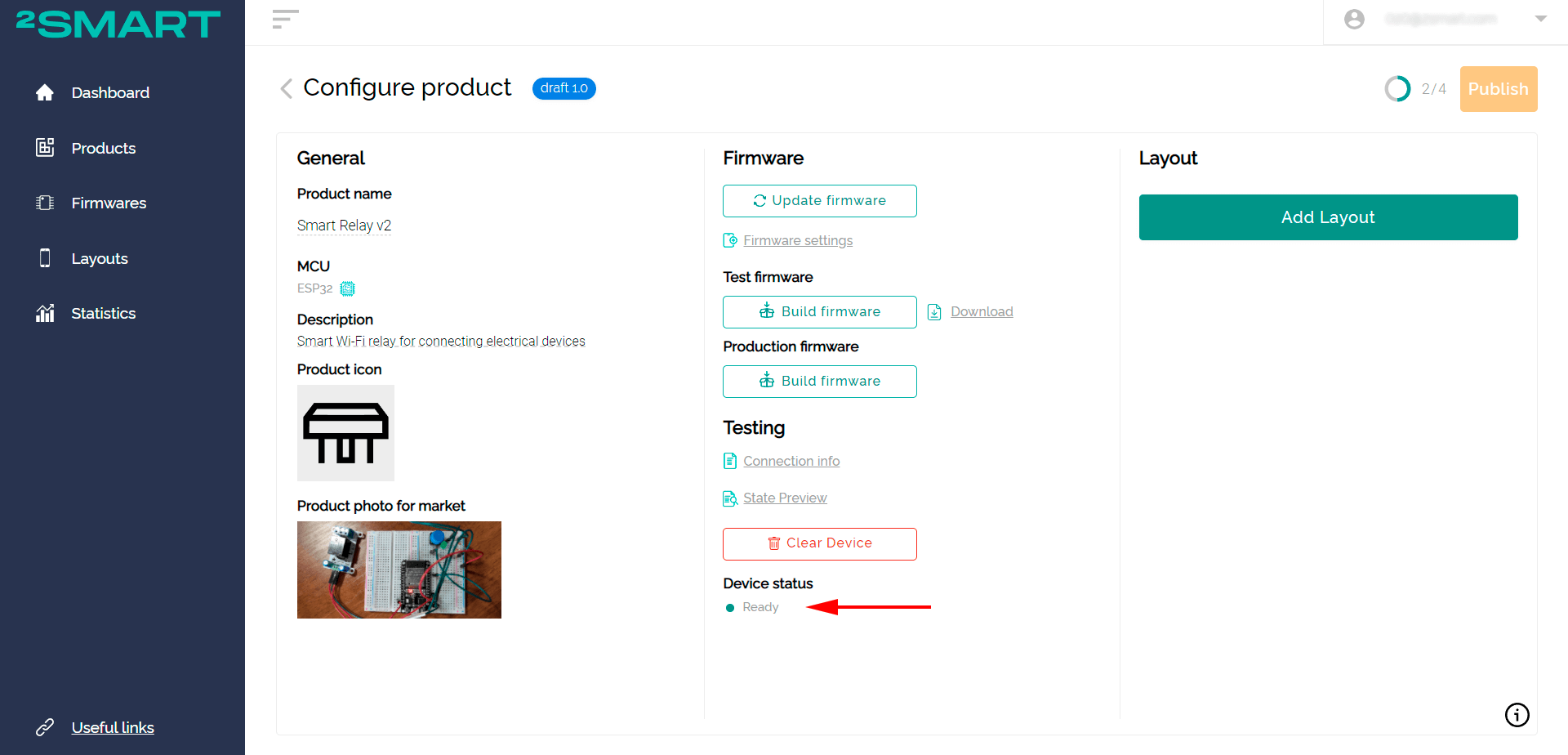
After flashing is completed, return to your 2Smart Cloud account and wait until the device is detected by the platform. If this does not happen within one to two minutes, unplug your device and plug it back into the Mac.
The device's "Ready" status indicates that the prototype has been successfully connected to the platform.
When getting confirmation that your connection to the prototype platform with test firmware was successful, you can continue working on your product. A similar approach (steps 5 and 6) is used to install the production firmware on finished devices.